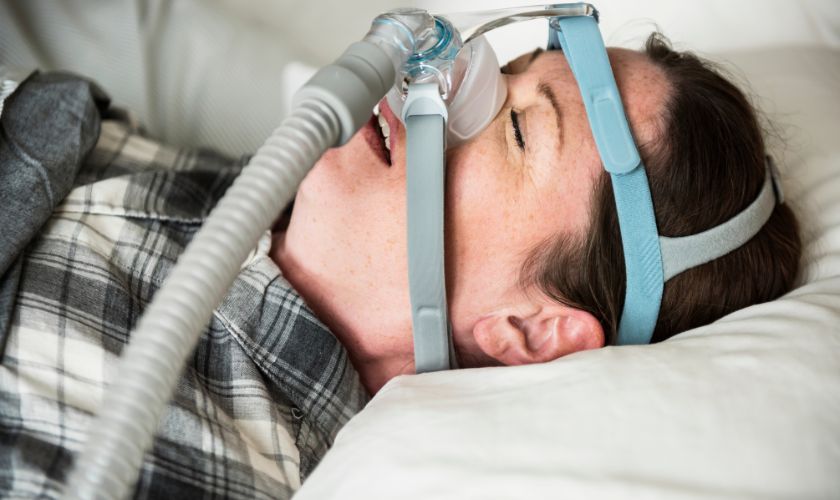
Many people think snoring and sleep apnea are the same. However, they are not identical sleep disorders. While both involve breathing issues during sleep, their causes, symptoms, and risks differ significantly. Understanding the difference can help you take action early and protect your overall health. Let’s break down how snoring and sleep apnea compare—and why the distinction matters.
What Is Snoring?
Snoring happens when air flows past relaxed throat tissues. This causes those tissues to vibrate. As a result, you hear that familiar snoring sound. It can be soft or very loud. Snoring often increases with age, weight gain, or alcohol use before bed. Although annoying, snoring doesn’t always indicate serious health issues. However, persistent snoring may suggest an underlying problem, such as obstructive sleep apnea, in Florham Park.
What Is Sleep Apnea?
Sleep apnea is a serious medical condition involving repeated breathing pauses during sleep. Most commonly, the airway becomes partially or entirely blocked. The most common type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), which occurs when the throat muscles collapse. During these episodes, oxygen levels drop, and the brain briefly signals you to wake up. Although you may not remember waking up, this severely disrupts your sleep quality. If untreated, sleep apnea increases the risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes.
How Are Snoring and Sleep Apnea Different?
Snoring involves noisy breathing. However, sleep apnea involves actual pauses in breathing. Although many people with sleep apnea snore, not all snorers have sleep apnea. Unlike simple snoring, sleep apnea leads to poor sleep and serious health risks. Another key difference is that snoring rarely causes daytime sleepiness, while sleep apnea often does. Also, sleep apnea frequently includes choking or gasping sounds during the night. If these symptoms appear, medical evaluation becomes very important.
Warning Signs of Sleep Apnea
Recognizing symptoms early helps prevent complications linked to sleep disorders like sleep apnea.
Here are common signs of sleep apnea to watch for:
- Loud, chronic snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Frequent night awakenings
- Dry mouth or sore throat upon waking
- Morning headaches
- Excessive daytime fatigue
- Difficulty concentrating
If you notice several of these signs, consult a sleep specialist immediately. The sooner you seek help, the better your chances for effective treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Doctors often diagnose sleep apnea using a sleep study, either at home or in a lab. This test monitors your breathing, oxygen levels, and sleep patterns overnight. If diagnosed with sleep apnea, several treatment options are available. The most common is CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure), which keeps your airway open. Other options include oral appliances, weight loss, surgery, or lifestyle changes. Simple snoring may improve with sleeping position changes or reduced alcohol intake. In contrast, sleep apnea requires ongoing medical care and attention.
When Should You Seek Help?
If snoring disrupts your life or includes gasping, you should speak to a doctor. Also, if you feel tired despite sleeping all night, get evaluated for sleep disorders. Left untreated, sleep apnea can harm your heart, brain, and daily functioning. Fortunately, treatment often improves both sleep and quality of life quickly. Don’t wait—getting answers starts with a simple conversation with your healthcare provider.
Sleep Better and Live Healthier
Although they may sound similar, snoring and sleep apnea are very different sleep disorders. Snoring can be harmless, but sleep apnea poses serious health risks if ignored. Knowing the signs and taking action protects your health and sleep quality. Treatment options exist for both conditions, especially when diagnosed early. Therefore, never ignore loud snoring, gasping sounds, or extreme fatigue. Your sleep matters—your life depends on it.